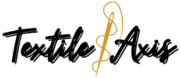Polypropylene (PP) Fiber
Types, Preparation, Properties and Application
Polypropylene Fibers/What is Polypropylene Fiber?
Polypropylene belongs to the group of polyolefins and is partially crystalline and non-polar.
Polypropylene (PP) is a thermoplastic polymer, used in a wide variety of applications.
Its properties are similar to polyethylene, but it is slightly harder and more heat resistant.
Polypropylene chemical formula is (C₃H₆)ₙ
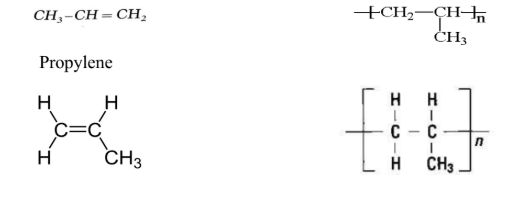
Types of Polypropylene
This polymer tacticity has defined by The Textile Institute in the following manner:
“An atactic polymer is defined as a planar projection of whose structure has the same substituents situated randomly to one side or the other of the main chain.”
“An isotactic polymer is defined as, a planar projection of whose structure has the same substituents situated uniformly on the same side of the main chain.”
“A syndiotactic polymer is defined as a planar projection of whose structure has the same substituents situated alternately on either side of the main chain.”
Preparation of Polypropylene
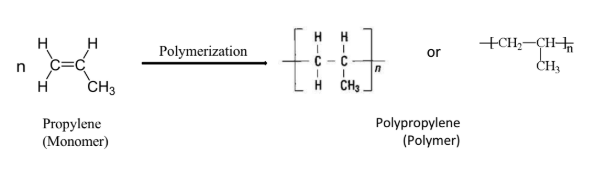
PP is prepared from the monomer propylene.
Commercial PP is produced from its monomer propylene using the Ziegler-Natta process.
A typical may be prepared by reacting titanium trichloride (TiCl4) with aluminum triethyl (AlEt3) in Naptha under nitrogen to from a slurry consisting of about 10% catalyst and 90% Naptha.
The conversion of propene to polypropylene is an exothermic reaction.
The general reaction for polymerization of propene is as follows-
Properties of Polypropylene
PP is a thermoplastic polymer.
The thermal expansion of PP is very large but somewhat less than that of PE.
It is the lightest known homopolymer.
It is a linear hydrocarbon polymer.
At room temperature is resistant to fats and almost all organic solvents, apart from strong oxidants.
Non-oxidizing acids and bases can be stored in containers made of PP.
It is slightly susceptible to oxidative attack.
It has excellent moisture resistance.
Isotactic PP has a high melting point of about 160–170°C
Application of Polypropylene
- PP is most commonly used for plastic molding.
- Typical molding includes bottle tops, containers, toys, refrigerator, machine parts, TV, radio, computer cabinets, fittings, luggage, stacking chairs, laboratory equipment, washing machine parts, car battery case, etc.
- It is used to producing packaging films, ropes, storage tanks, seat covers, etc.
- Polypropylene is used in the manufacturing of piping systems.
Because of high-temperature resistance, PP can be used to prepare to sterilize trays, funnels, pails, bottles, and instrument jars for medical application because it can withstand the heat in an autoclave.
PP is used in furniture items such as chairs, tables, bedside tables, cupboards, etc.
PP is used as insulation for electrical cables.
Fiber (yarn and textile) can be formed using PP.