Jute Cultivation, Classification, and Grading Standards
Jute Fiber
Jute fibers are obtained from the genus Corchorus of the order Tilliaceae . There are two species of the order cultivated for the sake of this fibers namely Corchorus capsularis and Corchorus olitorious . Jute is now produced in greater quantity than any natural textile fiber other than cotton. Jute was first spun in Dundee in 1828 .
Jute has been cultivated mainly in India. Bangladesh and Thailand. Jute is also grown in Burma, Chaina, Brazil , Nepal and Formosa , but at present their production is negligible compared with that of the three main jute producing countries .
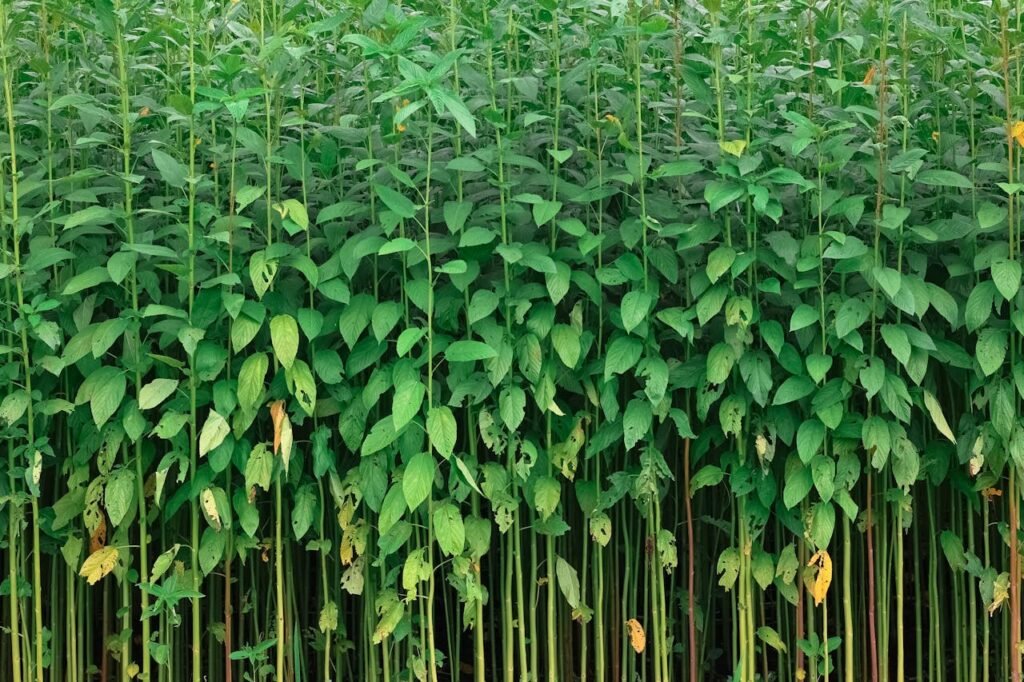

Cultivation Process of Jute Fiber
Jute grows well in tropical countries having much rainfall and hot climate. Bangladesh is the real home for growing the best quality of jute.
Jute plants need a moist climate and swampy land for their growth. The cultivation of jute is a difficult process . The land is ploughed , harrowed and manure well before sowing seeds . Generally the seeds are sown in march and april after a shower . When the plants grow up a little , the fields are weeded out for several times. In three or four months the plants are matured . The plants grow to a height of 6 to 12 ft and the steams are harvested shortly after the flowers are appeared . They are retted by immersion in water during periods varying from 12 to 25 days . The fibers are then separated from the residue of the steam by manual labour . The fibers are then washed in water and dried in the sun . In this way the fiber of jute is obtained and make ready for sale and use .
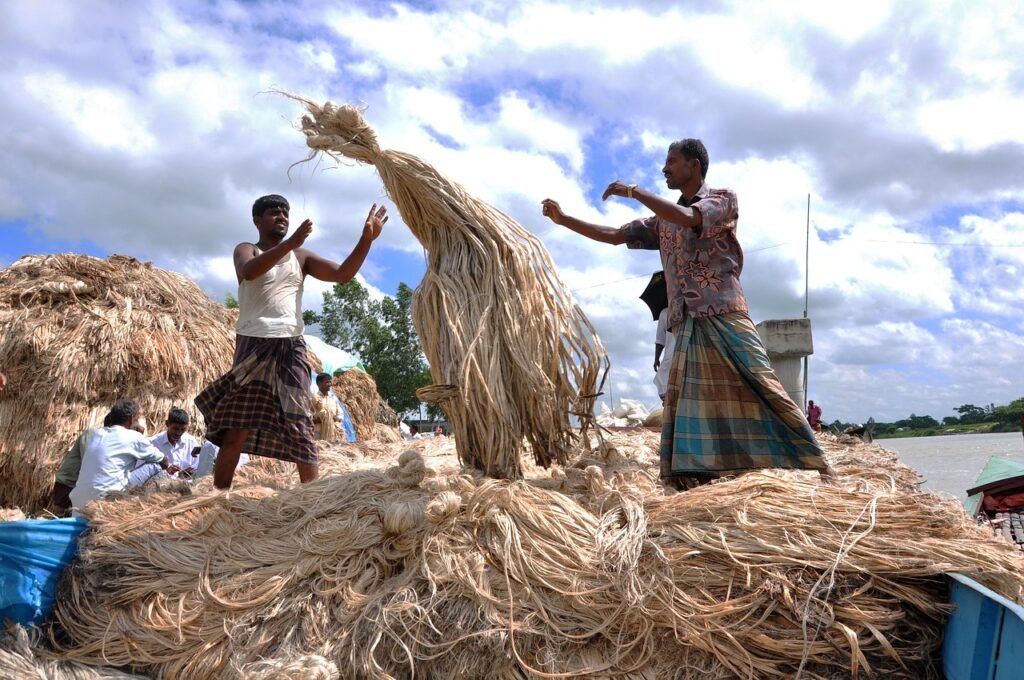

Classification of Jute Fibers / (Geographical distribution of jute in Bangladesh )
According to quality jute may be classified as –
1. Jat
2. District
3. Northern
JAT : This type of jute fiber grows in the district of Mymensingh , Dhaka and Comilla . These are famous for their best quality . It can be possible to produce strong, fine and lusturous fiber from this type of jute .
DISTRICT : District jute are two types :
1. Hard district
2. Soft district
The hard district jutes are better than soft district . Hard district jute mainly grows in Faridpur and soft district jute grows in Noakhali , Pabna , lower comilla and part of Dhaka .
NORTHERN : The variety of jute is mainly low quality , hairy and little lusture . Some qualities are vary rooted and dark color . This jute is grown in the district of Rajshahi , Dinajpur , Bogra , Pabna and between the river Gange and Bramaputra .

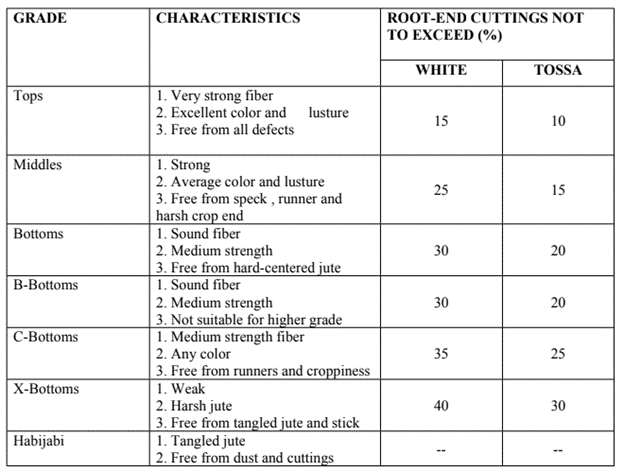
Grading of Jute Fiber (PUCCA JUTE)
The factors which are taken into account during grading are color , length , fineness of the fiber, lusture , strength , cleanness , freedom from defects and the amount of root end which will have to be cut off. Basically the Bangladeshi Jutes are classified into the following two types:
1. Bangla White ,
2. Bangla Tossa.
A ) WHITE JUTE
Bangla white special ( BW-S ) :
1. White creamy color
2. Finest texture
3. Very good lusture
4. Very clean
5. Completely free from any defect and red ends .
Bangla white – A ( BW – A ) :
1. White to light cream color
2. Fine texture
3. Strong and very good lusture
4. Clean
5. Free from red ends and any blemish
Bangla white – B ( BW – B ) :
1. Light cream to straw color
2. Texture
3. Strong and good lusture
4. Clean
5. Well hackled and free from red ends
Bangla white – C ( BW – C ) :
1. Light gray or light reddish to straw color
2. Sound strength
3. Average lusture
4. Clean and free from croppy or hard gummy tops and roots
Bangla white – D ( BW – D ) :
1. Any color
2. Average strength
3. Occasional bark and specks permissible
4. Slightly croppy and gummy tops permissible
5. Red ends also permissible
Bangla white – E ( BW – E ) :
1. Any color
2. Any strength
3. Free from perished fibers
4. Unretted jute and sticks.
B ) TOSSA JUTE
Bangla tossa special ( BT – SPECIAL ) :
1. Uniform reddish / Golden color
2. Fine texture
3. Very strong
4. Very good lusture
5. Clean cut and well hackled
6. Completely free from any defects
Bangla tossa A ( BT – A ) :
a. 1. Grey to golden color
2. Fine texture
3. Strong and good lusture
4. Clean cut and well hackled
5. Completely free from any defects
b. 1. Uniform light golden to reddish color
2. Fine texture
3. Strong and good lusture
4. Clean cut and well hackled
5. Completely free from any defects
Bangla tossa B ( BT – B ) :
a. 1. Light to medium grey color
2. Sufficient clean
3. Good texture
4. Good lusture
5. Clean cut and well hackled
6. Free from any defects
b. 1. Light grey / Reddish color excluding dark grey
2. Sufficient clean
3. Good texture
4. Good lusture
5. Clean cut and well hackled
6. Free from any defects
Bangla tossa C ( BT – C ) :
1. Mixed color
2. Average strength
3. Occasional bark and soft specks allowable
4. Free from runners
5. Slightly croppy and gummy tops permissible
6. Well cut and hackled
7. Free from black root ends
Bangla tossa D ( BT – D ) :
1. Mixed color
2. Average strength
3. Occasional bark and soft specks allowable
4. Free from runners
5. Slightly croppy and gummy tops permissible
6. Rough cut and hackled
7. Free from black root ends
Bangla tossa E ( BT – E ) :
1. Any color
2. Any strength
3. Free from unretted jute and sticks
4. Free from perished fiber
5. Rough cut and hackled
6. Bark and dark center permissible

KUTCHA BALERS GRADING OF RAW JUTE